CATHODE RAY TUBE DISPLAYS or CRTs
The Cathode Ray Tube “has evolved from the triode structure of the Braun tube, which was the first scanning version of the device in the late 1890’s.” [18] The Cathode Ray Tube, a light-emitting display, has been a highly successful commercial product, and provided a low price point for designers of panoramas based on lowered cost attributed to mass production in the global economy.
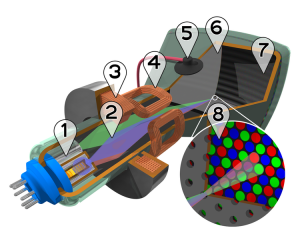
Cathode Ray Tube Displays, abbreviated CRT, “is a vacuum tube containing an electron gun (a source of electrons) and a fluorescent screen, with internal or external means to accelerate and deflect the electron beam, used to create images in the form of light emitted from the fluorescent screen. The image may represent electrical waveforms (oscilloscope), pictures (television, computer monitor), radar targets and others.” [4]
“The CRT is able to use relatively simple architecture and control electronics to display high-performance video and data in a low-cost and highly manufacturable component.” [18] Ironically the simple architecture and voluminous size that made the CRT an easily manufactured and distributed product also began to create industry trepidation because the breadth of distribution expenses accrued from the magnitude of shipping weight.
Cathode Ray Tube Displays lack flexibility because a rigid screen and housing volume needed to host the vacuum tube. “Various attempts to squeeze the traditional 3-D CRT into two dimensions or at least reduce the depth substantially have been unsuccessful to date.” [18]
This inflexibility based on mere physical stature has led to the decrease of demand for commercial innovation and corporate backing with Cathode Ray Tube Displays. “In 2005 Sony announced that they would stop the production of CRT computer displays. Similiarly, German manufacturer Loewe ceased production of CRT TVs.”[4] These trends lowered manufacturer confidence and increased enthusiasm for thinner housing for the viewing device and flexibility desired in residential and commercial environments.